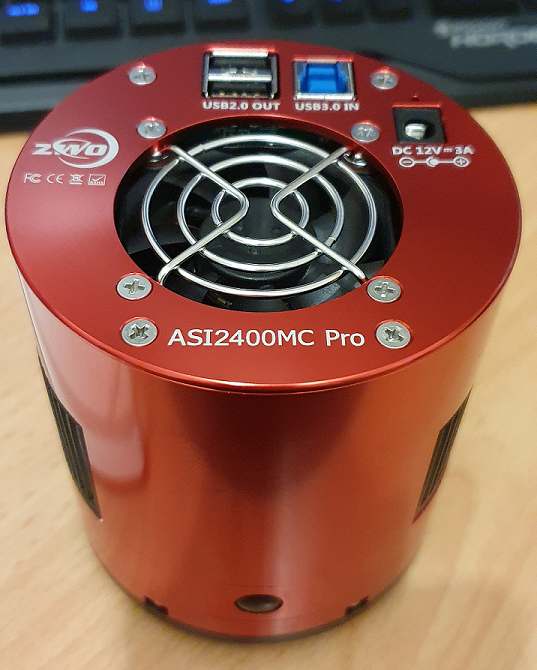
I was lucky enough for 365Astronomy to offer me one of the ZWO ASI2400 full frame cameras to test and write a review, so obviously I jumped at the chance, and within a couple of days I was successfully imaging and acquiring data with it, so firstly what is the ASI2400?
The ASI2400MC Pro is a full frame 24mpx camera that utilises the Sony IMX410 back illuminated sensor, ZWO produced a similar camera before which was the ASI128MC Pro (24mpx) and they also have the ASI6200 (62mpx), so what are the differences between the cameras?
| ASI2400MC | ASI128MC | ASI6200MC | |
| Image Sensor | IMX410 | IMX128 | IMX455 |
| Pixel Size | 5.94 | 5.97 | 3.76 |
| Full Well Capacity | 100ke | 76ke | 51.4ke |
| Cooling Delta | -35C | -35C | -35C |
| Resolution | 6072×4042 | 6032*4032 | 9576×6388 |
| ADC | 14-Bit | 14-Bit | 16-Bit |
| Read Noise | 1.1e-6.4e | 2.5e | 1.2e-3.5e |
| DDR Buffer | 256MB | 256MB | 256MB |
| QE | >80% | >53% | >80% |
| FPS (Video) | 8 | 5 | 2 |
If we compare the ASI2400 and the ASI128 since they have similar pixel sizes and offer almost a matching resolution, but the ASI2400 clearly is a better camera, with a higher full well capacity, this means that it takes a lot more to saturate out the colours around bright stars for example, but also a big increase on the quantum efficiency going from 53% to >80%.
Now the first thing I noticed was that the ASI2400 was only slightly cheaper than the ASI6200, but the ASI6200 is offering a much higher resolution, so why would people not just go for the ASI6200? Well it comes down to pixel size, the ASI6200 has a pixel size of 3.76 so it would be better suited to a short focal length scope, if I attach the ASI6200 to my SharpStar 15028HNT which has a focal length of 420mm at F2.8, this will give me around 1.85 Arc-Seconds per Pixel which for UK skies is an ideal figure, the ASI2400 has a bit more flexibility with the focal length of telescopes because of the larger pixel size, so whilst the ASI6200 offers a higher resolution image sensor of 62mpx, the ASI2400 offers more flexibility of a higher focal length telescope.
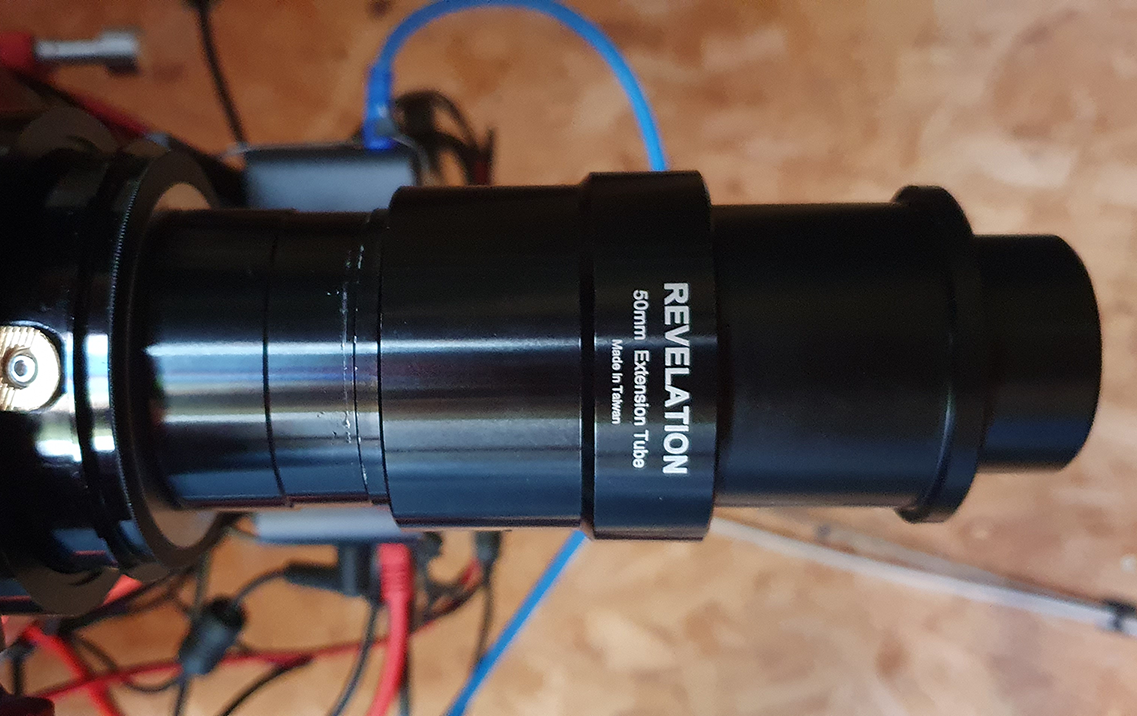
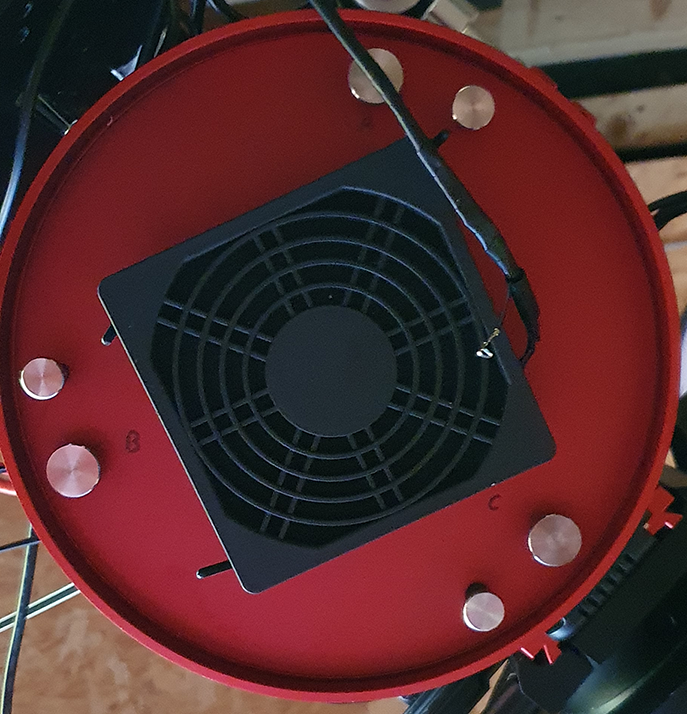
When I unboxed the ASI2400 I was very impressed with the quality, this was the first ZWO Camera I have ever actually seen in the flesh, the red finish matches my SharpStar 15028HNT, but one thing that I noticed straight away was the two additional USB Ports on the top of the camera which I sat and thought to myself that it would certainly help with tidying up my cables around the scope. In the box was a couple of adapters to obtain the very common 55mm back focus, two USB Cables, and a USB 3.0 cable, and the camera arrived in a very nice case too.
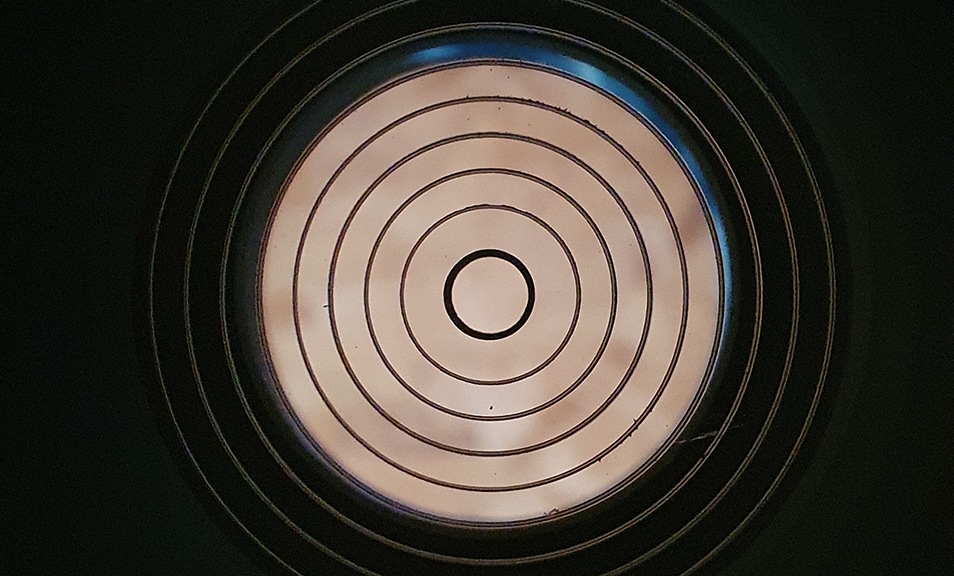
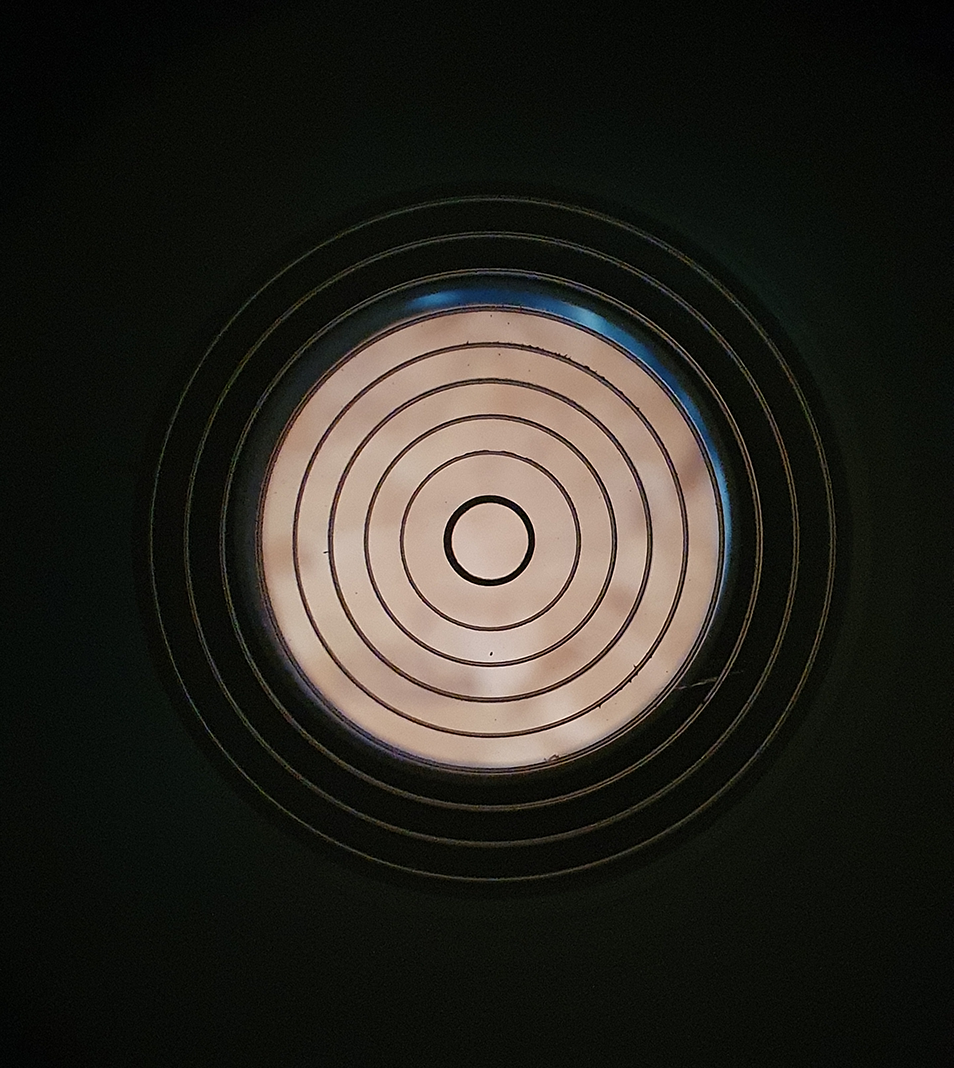
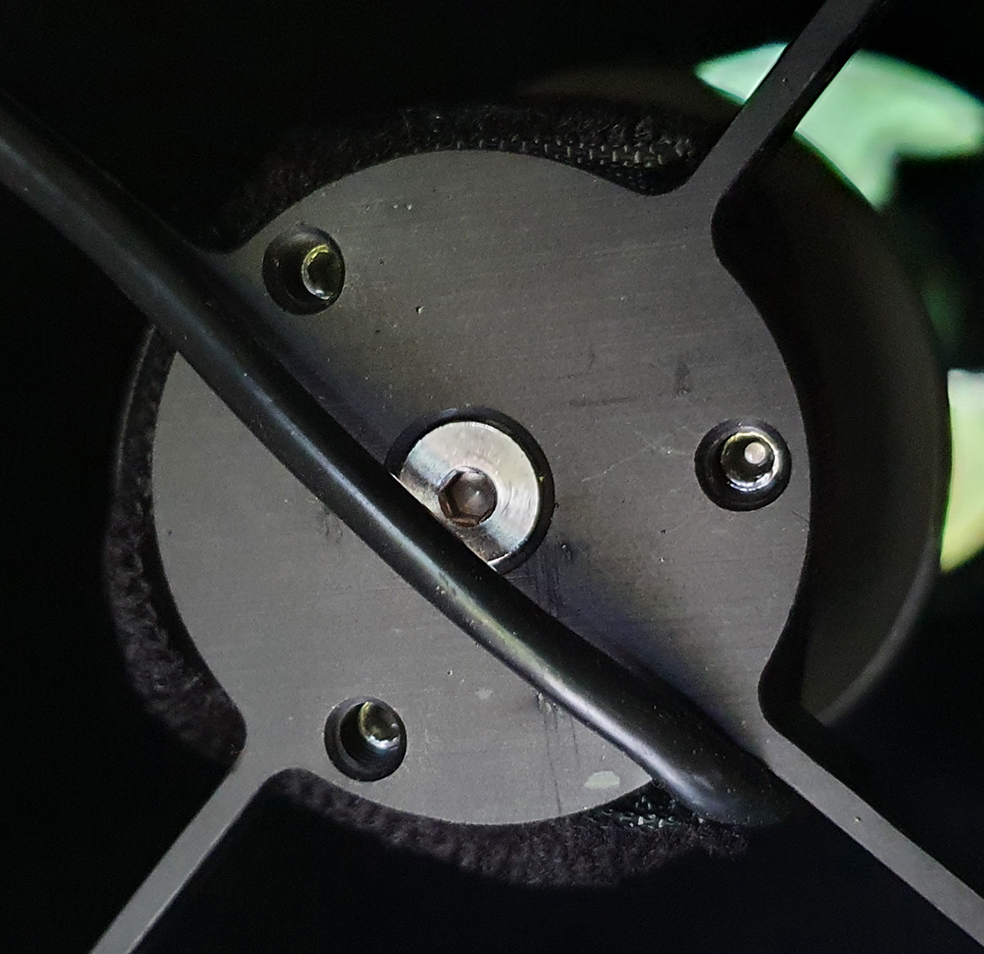
I removed the camera sensor cover and revealed the massive full frame sensor and compared it to the APS-C sized camera I have and was like wow, that’s a big sensor, here’s a picture of the sensor:
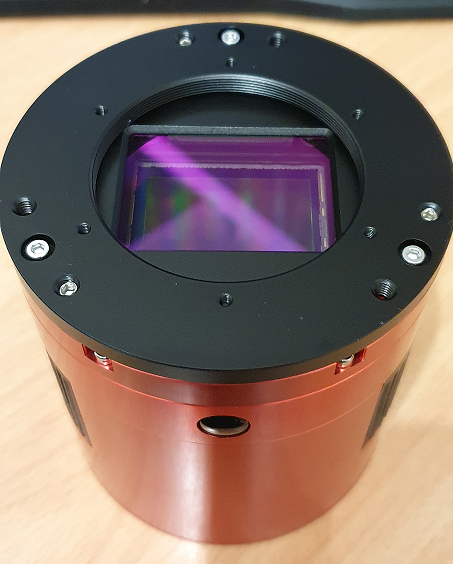

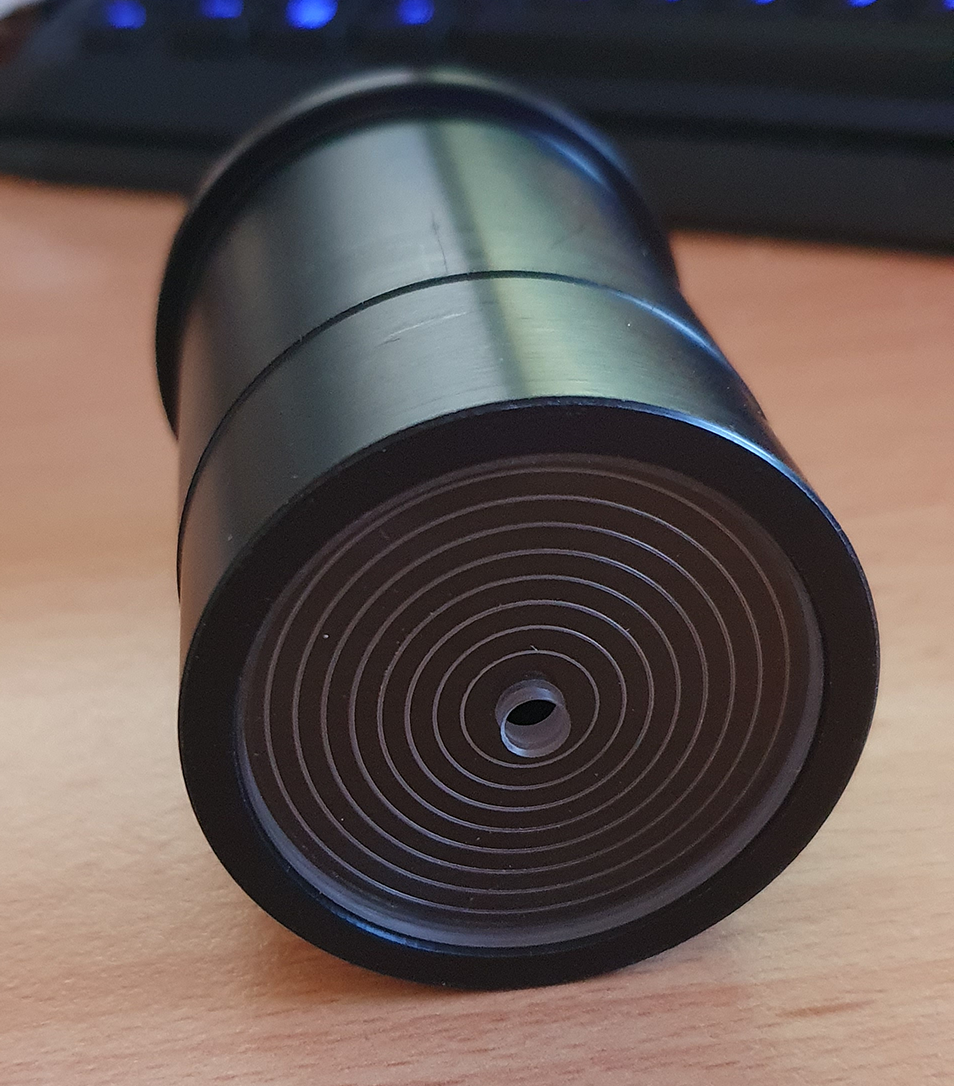
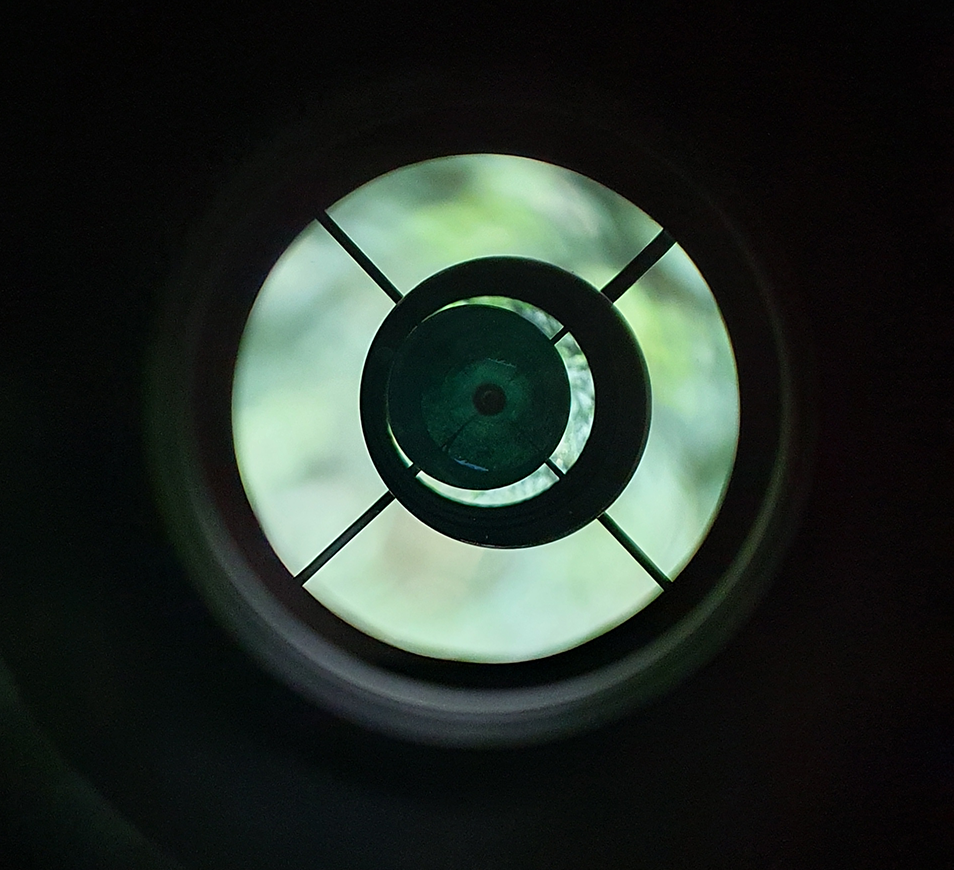
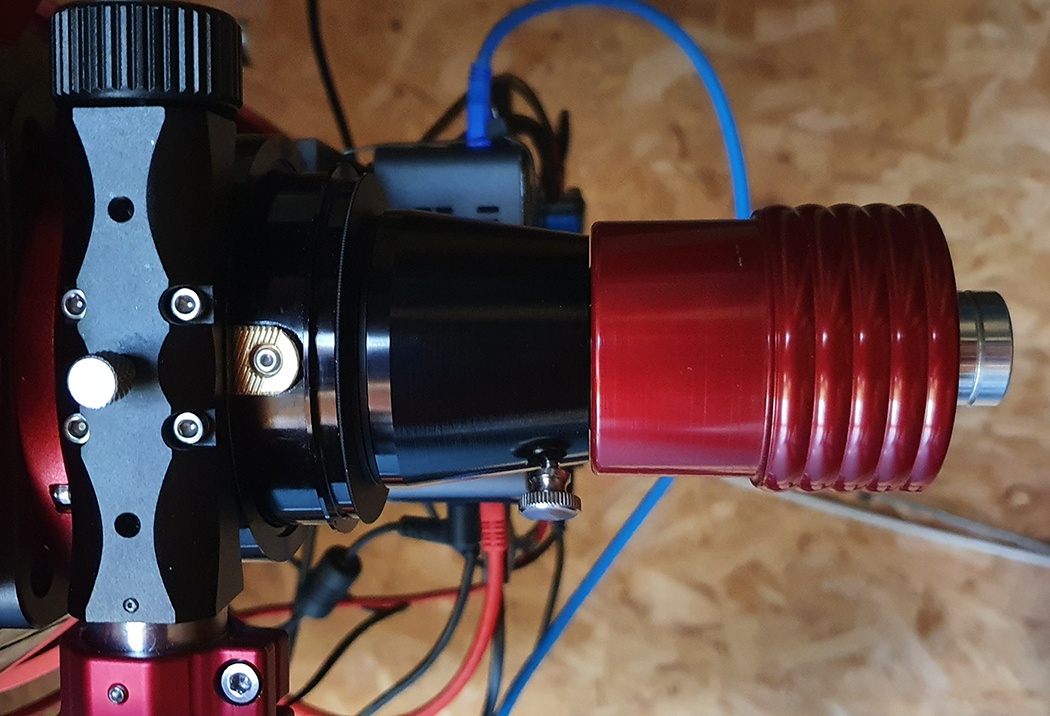
I noticed too that there was a special tilt plate on the camera which in my opinion is a critical point, my other camera has a tilt plate that is very cumbersome to use, so after a while of looking at the sensor, I decided to start adding my ZWO filter drawer and M48 extension tubes in order to get it connected to the mount, I am using the ZWO M54 2″ Filter drawer which has a 2mm M54 to M48 adapter too, threading the filter drawer on the camera was very smooth, but I would not expect anything less than that with ZWO kit connecting to ZWO kit, here’s a picture with the filter drawer and the Optolong L-Pro 2″ filter connected to the camera:
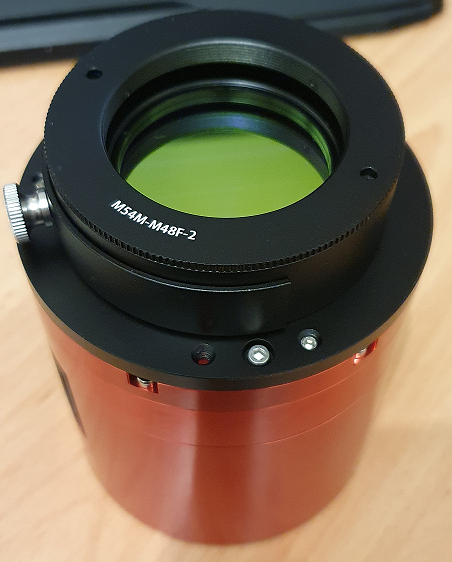

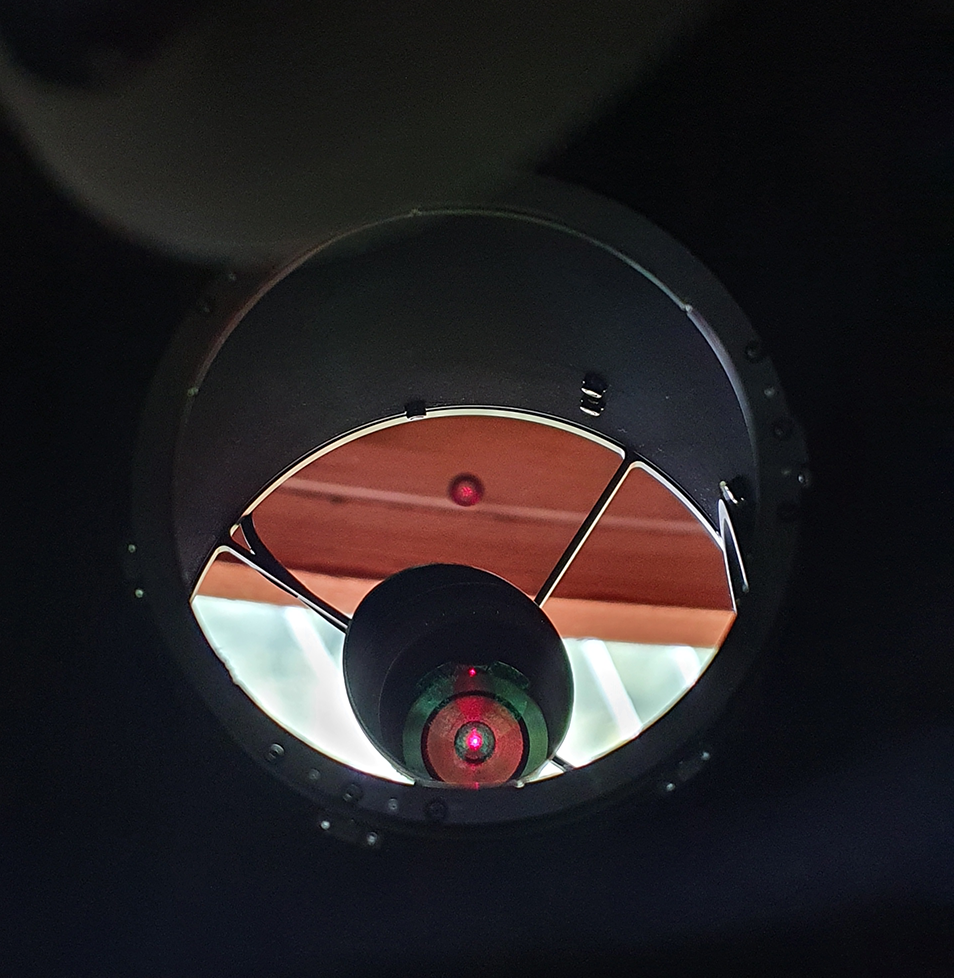
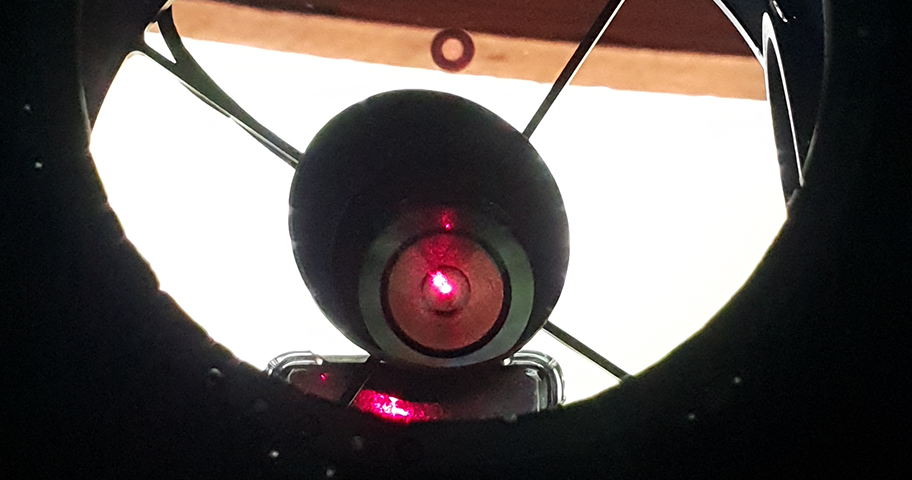
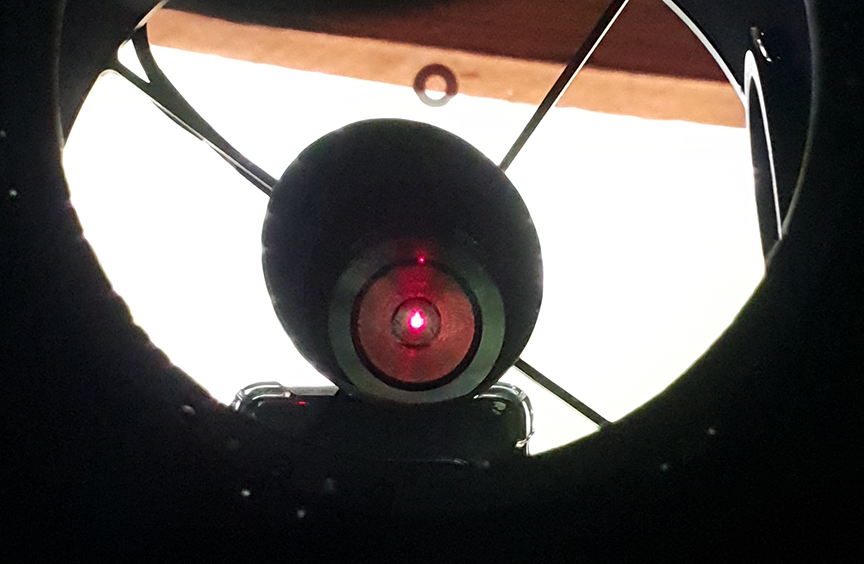
Once connected to the telescope, I had to find out where the camera was facing when connected at the optimal distance of 55mm as all of my image train is threaded on, once identified which direction the top of the camera sensor was facing I could rotate the focuser and then re-check the collimation with the laser before putting the camera back on and connecting the cables.
Identifying which side of the camera the top of the sensor was is so easy on this camera, there’s what looks like a black plastic button on the side of the camera, it is obviously a cover of some sort, but this also indicates which side the top of sensior is located, something I wish all camera vendors would do.
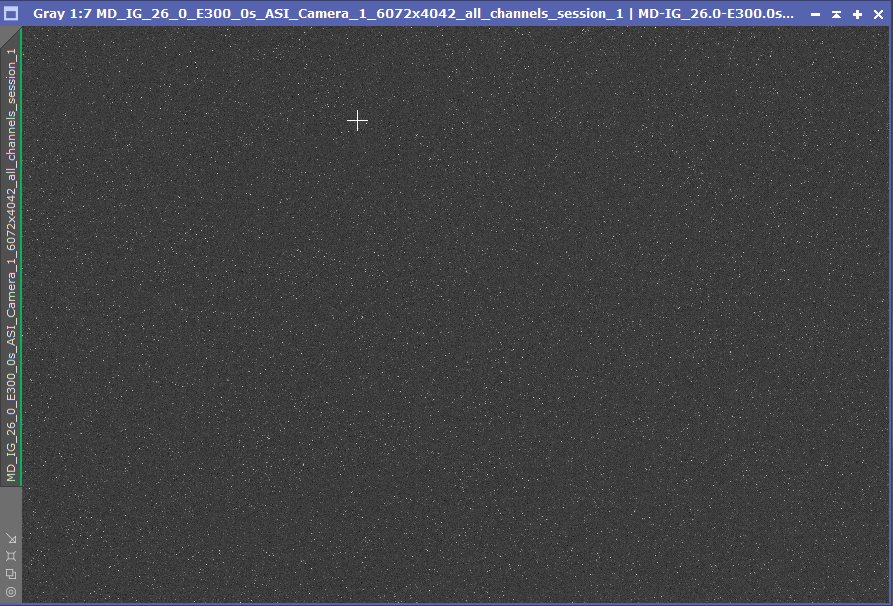
One of the first things I do when testing out a new camera is dark frames, all vendors claim they have zero amp glow, so this is always my first test, and the ASI2400 didn’t let me down, indeed there was zero amp glow and I tested with various exposure times and gain settings, here’s a 300S exposure with Gain 26 which has had a Screen Transfer Function auto stretch applied:
After connecting it all up to the telescope, and acquiring some darks, flats, and BIAS frames, and the skies were clear, it was time to put the camera under a proper test, I had set a couple of targets up, the Cygnus Loop and the Elephant’s Trunk Nebula using the Optolong L-eXtreme Narrowband filter and here are the results:
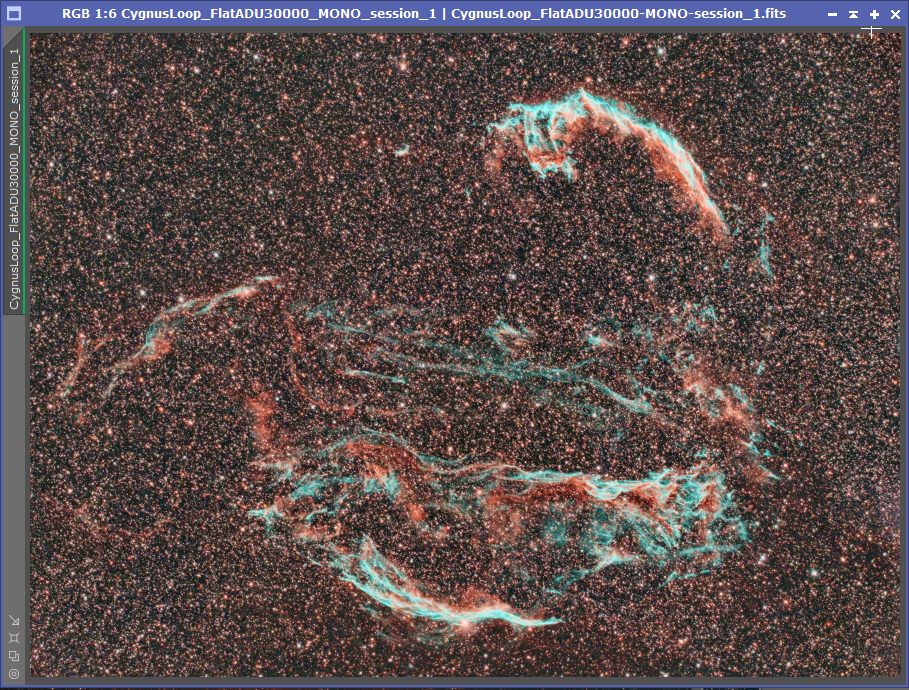
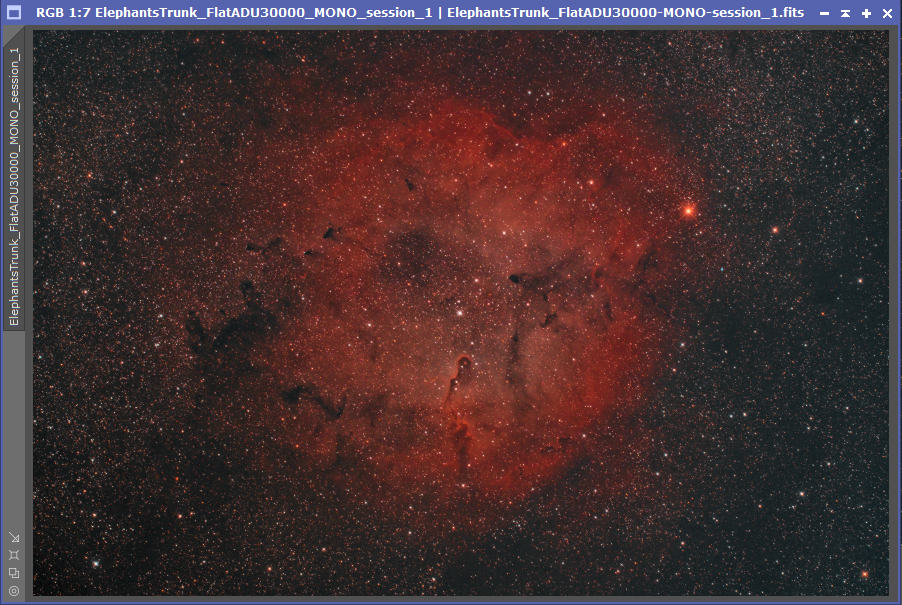
So you can see the camera performed really well, stars are almost perfect in the corners (a little fine tuning required on spacing), I am hoping to get a few more clear nights over the next few days to build on the above images and really show off the performance of the ASI2400, and I can’t wait to test it out on the Iris Nebula.
Conclusion:
The ASI2400 is in my opinion an awesome piece of kit, that massive full frame sensor has the adaptability for longer focal length telescopes due to the larger pixel size, the advantage of the USB Hub built into the camera, the adjustable tilt plate on the front of the camera is the most advantageous aspect, would have saved me so much time trying to rectify tilt instead using copper shims, but also the smaller things that are equally as important like having something to identify which way round the sensor is rather than trying to figure it out with images in my opinion is what sets this apart from other similar cameras from other vendors.
If you are looking for a full frame camera and have a short focal length telescope, the ASI2400 or the ASI6200 full frame cameras will do just the job,but any longer focal length scopes, then the ASI2400 is the right choice.
Additional image taken since writing this post: